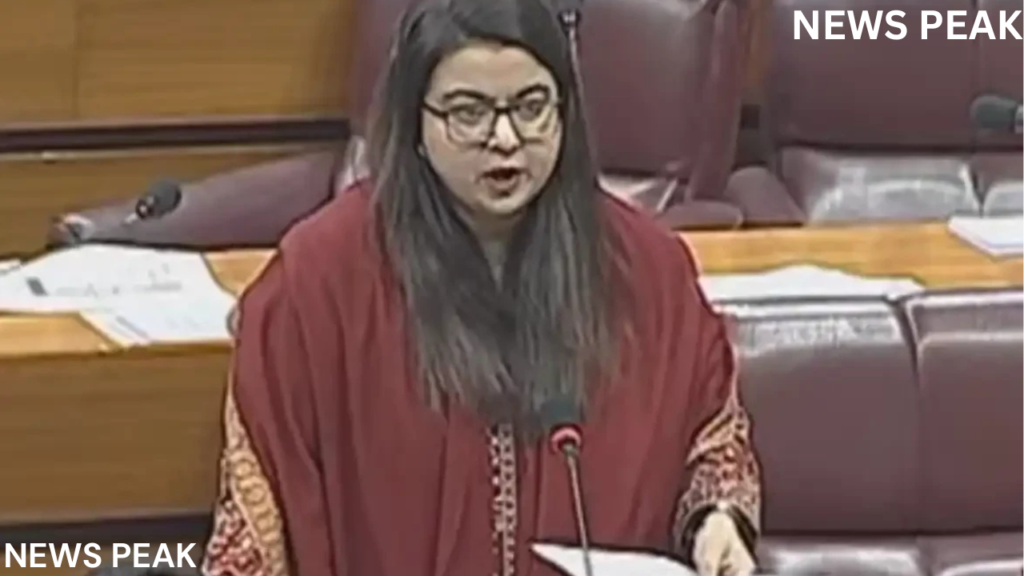
The Digital Nation Pakistan Bill, 2024 was presented by the federal government to the National Assembly on Monday.
Shaza Fatima Khawaja, the Minister of State for IT and Telecommunication, introduced the law, which sought to centralize social, economic, and governance data and give residents a digital identity.
In June, the federal cabinet gave its approval to the law.
In order to accelerate sustainable economic development, improve the well-being of citizens, and modernize governance frameworks for effective and efficient public service delivery, the bill, a copy of which is available on Dawn.com, stated that it was expedient to enable the people to become a digital nation by utilizing the transformative power of digital technologies, responsible data use, innovative service delivery models, and robust digital public infrastructure.
It also stated that it was time to build a prosperous digital economy, a forward-thinking digital society, and a collaborative digital governance ecosystem with safe, open, and interoperable digital public infrastructure as a major enabler of innovation, connectivity, and smooth cross-sector integration.
According to the bill, the creation of the Pakistan Digital Authority and the National Digital Commission was essential in order to accomplish the aforementioned goals because they would offer the operational control, governance, and strategic direction needed.
The bill states that the prime minister leads the National Digital Commission (NDC), which is composed of the four chief ministers and the leaders of the State Bank, Federal Board of Revenue, and Pakistan Telecommunication Authority. Meanwhile, the Pakistan Digital Authority (PDA) would be led by the top.
According to the bill, in order to accomplish the goals of a digital nation and match the country’s digital transformation with economic growth, efficient governance, and societal development, the NDC would prescribe the necessary policies, provide governance, and guarantee the necessary coordination among federal, provincial, and sectoral bodies.
In order to guarantee a cohesive and cooperative approach to digital transformation across all governmental levels, the bill lists the NDC’s primary responsibilities as approving the national digital masterplan and its implementation plans, giving the PDA strategic direction and governance, and coordinating with all pertinent federal, provincial, and regulatory bodies.
In order to ensure a unified digital agenda, eliminate redundancies, and maximize resource efficiency, the bill defined the national digital masterplan as the comprehensive strategic blueprint to turn Pakistan intoThis would serve as the main framework guiding digital initiatives, regulatory standards, and guidelines.
In order to address interjurisdictional issues and facilitate effective implementation, the NDC would also need to issue directives to entities to align their strategic direction, policies, operations, and digital initiatives with the national digital masterplan. It would also need to make sure the PDA had the necessary resources, enabling conditions, and support to carry out the masterplan effectively. Finally, it would need to review instances of non-compliance with the masterplan that were referred by the PDA or NDC and may grant exceptions or issue additional.
To guarantee alignment with the NDC’s strategic guidelines, the PDA would create, carry out, oversee, and update the national digital masterplan on a regular basis. This would include sectoral and implementation plans.
Among its other duties are similar tasks associated with the masterplan’s operations, such as making sure that the plan is followed; helping stakeholders coordinate; creating a framework for evaluating projects under the masterplan; reviewing plans that are pertinent to the masterplan; creating and implementing a national data strategy and comprehensive data governance framework in government agencies and the public and private sectors; advising on the governance, standards, and operational compliance of cloud infrastructure in the public sector; making sure that national cloud policies are followed; helping to develop a digital economy strategy; ensuring the creation, strategic oversight, and adoption.
A digital identification for all citizens is one of the main proposals of the incoming government. It would contain information on a person’s assets, health, and other social indices.
According to officials, the goal of the bill was to increase access to the offices that handle ID cards, birth certificates, land records, and health records.
Government departments would also be the focus of the digitization initiative, and they would get goal-oriented strategies to enhance services.
The new digital ID program will be similar to the programs that have been put in place in Estonia, India, and the United Arab Emirates.